Tong Cui, Danyang Yu, Weiling Piao, Huangzhao Wei, Xu Yang, Chenglin Sun*, Wenjing Sun*
Catalysis Letters ,2025,155(2)
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-024-04915-4
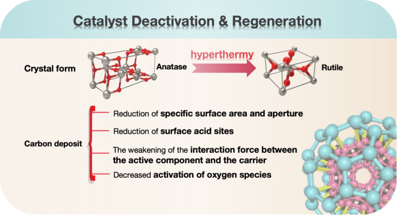
ABSTRACT: RuO2/TiO2, as the main catalyst in wet catalytic oxidation, faces the problem of catalyst deactivation while treating high concentration organic wastewater efficiently and without pollution. There have been many studies on catalyst deactivation and regeneration, but most of them are based on laboratory simulation environment. Due to the complexity of industrial environments, the causes of industrial catalyst deactivation are still unclear, while there are very few studies on regeneration. Herein, we characterized industrially used catalysts and found that the causes of catalyst deactivation can be attributed to two reasons, namely, the change of carrier crystal shape and carbon accumulation. Thermal regeneration to address the carbon accumulation problem restores some of the physicochemical properties of the used catalysts, however, thermal regeneration cannot restore the catalyst support phase from rutile back to anatase, resulting in the inability to restore catalyst activity. Therefore, the catalyst was regenerated by the method of direct addition of active components, and the catalyst activity was basically restored when the Ru mass fraction was 0.5%. Moreover, the method of directly adding active components has the advantages of simplicity and no energy consumption, which is easy to be utilized in the industrial production process.
摘要:RuO₂/TiO₂作为湿式催化氧化过程中的主要催化剂,能够高效且无污染地处理高浓度有机废水的同时,然而面临着催化剂失活的问题。目前已有许多关于催化剂失活与再生的研究,但大多数是基于实验室模拟环境进行的。由于工业环境的复杂性,工业催化剂失活的原因尚不明确,而关于再生的研究则非常少。本文通过对工业使用过的催化剂进行表征,发现催化剂失活的原因可归结为两点:载体晶型的变化和碳积累。通过热处理再生,碳积累问题可以部分恢复失活催化剂的物理化学性质,然而,热再生无法将催化剂载体物相从金红石相恢复为锐钛矿相,导致催化剂活性无法完全恢复。因此,采用直接添加活性组分的方法对催化剂进行再生,当Ru质量分数为0.5%时,催化剂活性基本恢复。此外,直接添加活性组分的方法具有简单、无能耗的优点,易于在工业生产过程中应用。


