Songbo He, Kenny Zuur, Dian Sukmayanda Santosa, Andre Heeres, Chuncheng Liu, Evgeny Pidko, Hero Jan Heeres*
Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 281:119467.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119467
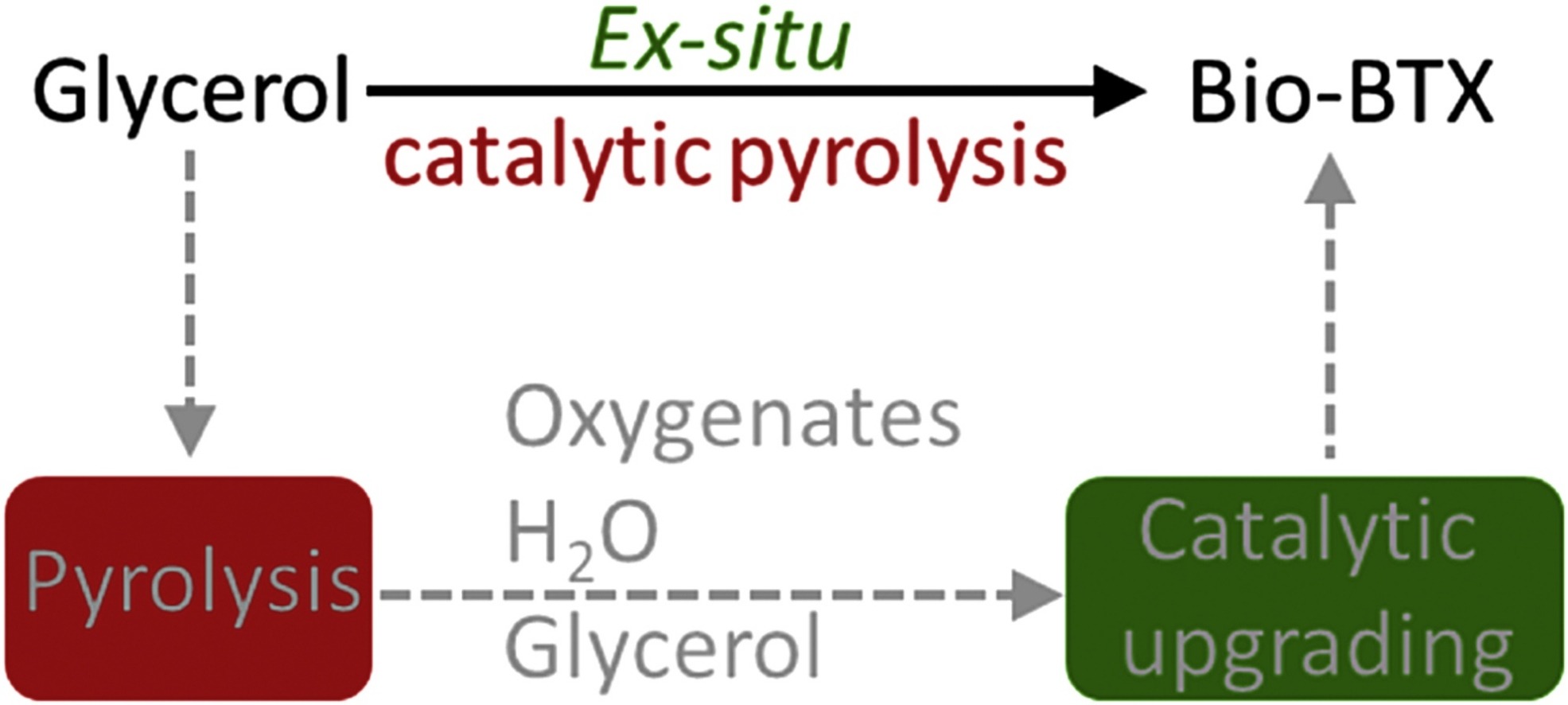
ABSTRACT:The catalytic conversion of pure glycerol to bio-aromatics (bio-BTX) over an un-modified H-ZSM-5 (SiO2/Al2O3 molar ratio of 23) via an ex-situ catalytic pyrolysis approach in a continuous tandem-micro reactor at a scale of 1 g glycerol h−1 was investigated. A BTX peak carbon yield of 28.1 ± 0.2 % was obtained at a pyrolysis temperature of 400 °C, catalytic upgrading temperature of 500 °C, atmospheric pressure and a WHSV of 1 h−1. About 70 % of the bound oxygen in glycerol was converted to water. The latter was mainly formed in the catalytic upgrading unit (70 %), though conversion of glycerol to other oxygenates with water formation was also observed in the pyrolysis unit. Catalyst deactivation occurs at a time scale of hours and is mainly due to coke deposition (12.0 wt.%) on the catalyst surface. An oxidative regeneration procedure to remove coke was applied and 5 cycles of reaction-regeneration were performed successfully, though a drop in activity was observed after each cycle due to irreversible catalyst deactivation. Characterization of the fresh, deactivated and regenerated catalysts by various techniques revealed dealumination of the H-ZSM-5 framework and resulted in a dramatic decrease in Brønsted acidity of the catalyst. Dealumination mainly occurred in the catalytic upgrading reactor and to a by far lesser extent during catalyst regeneration. This information is relevant for a better understanding of the process on a molecular level but also for scale-up studies, e.g. for the design of pilot plants.
摘要:本研究采用非原位催化热解策略,在未改性H-ZSM-5(SiO₂/Al₂O₃摩尔比为23)催化剂上,通过规模为1克甘油/小时的连续串联微反应器,实现了纯甘油向生物芳烃(苯、甲苯和二甲苯,即bio-BTX)的催化转化。在热解温度400 °C、催化升级温度500 °C、常压及重量空速1 h⁻¹的条件下,BTX峰值碳收率达到28.1 ± 0.2%。甘油中约70%的结合氧被转化为水,其中水主要生成于催化升级单元(占总水生成量的70%),但热解单元中亦观察到甘油转化为其他含氧化合物并伴随水的生成。催化剂失活发生于小时级别的时间尺度,主要原因为表面积碳(12.0 wt.%)。通过氧化再生去除积碳,成功完成5次反应-再生循环,但每循环后均因不可逆失活导致活性下降。对新鲜、失活及再生催化剂的表征表明,H-ZSM-5骨架发生脱铝,致使布朗斯特酸度急剧降低;脱铝主要发生于催化升级反应器,再生过程中脱铝程度显著较轻。上述结果不仅有助于在分子层面理解过程机制,也为放大研究(如中试装置设计)提供了关键依据。


