Tiantian Zhang, Álvaro González Rivas, Xavier Fragua Fernandez, Na Li, Eyerusalem Gucho, Lin Zhu, Anton Bijl*, Joan Llorens Llacuna*, Songbo He*
Renewable Energy, 236, 121429
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2024.121429
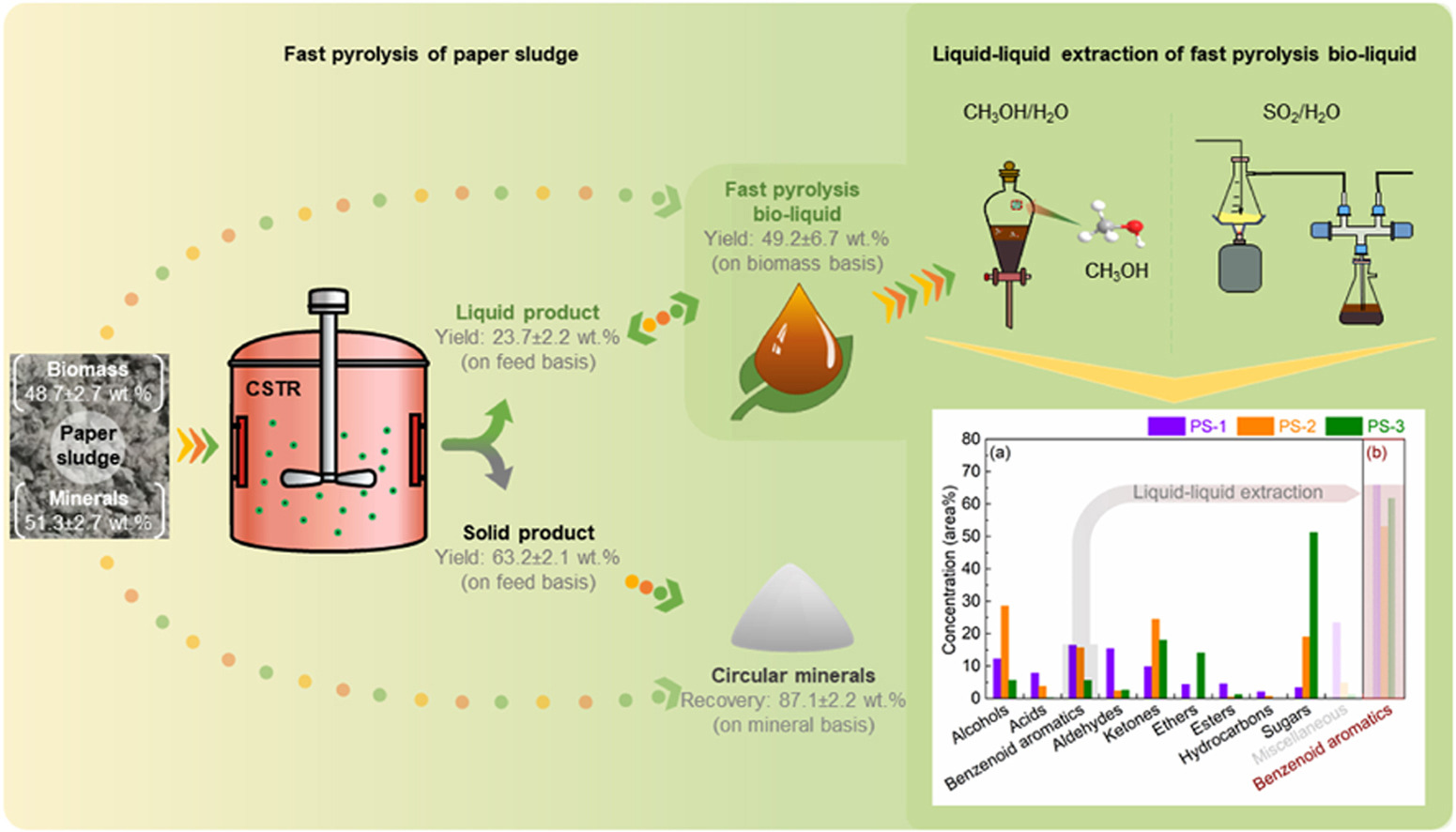
ABSTRACT: Paper sludge is a solid waste in paper mills and is conventionally treated by, e.g., landfill, composting, and incineration. Paper sludge contains paper production fillers and lignocellulosic biomass, both of which can be recycled to recover circular minerals and produce bio-based fuels and chemicals by, e.g., thermochemical recycling technology namely fast pyrolysis, for circular bioeconomy. In this paper, three different paper sludge samples collected in The Netherlands and Spain were analyzed by thermogravimetric analysis, moisture analysis, ash analysis, CHNS elemental analysis, powder X-ray diffraction, and X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Fast pyrolysis of paper sludge was carried out in a lab-scale continuous stirred tank reactor at 500 ± 10 °C with a paper sludge feeding rate of 1 kg h−1. The recovery of circular minerals, which are mainly calcium carbonate, is 87.1 ± 2.2 % (on mineral basis). The yields of fast pyrolysis bio-liquid and biochar are 49.2 ± 6.7 wt% (on biomass basis, equivalent to 23.7 ± 2.2 wt% on paper sludge basis) and 23.8 ± 8.3 wt% (on biomass basis). Fast pyrolysis bio-liquid is a diluted aqueous containing various oxygenates (major, including alcohols, acids, benzenoid aromatics, aldehydes, ketones, ethers, and esters) and hydrocarbons. Liquid-liquid extraction of the fast pyrolysis bio-liquid using CH3OH/H2O and SO2/H2O was further performed to obtain an improved bio-liquid with relatively high concentration of the desired bio-based chemicals (namely benzenoid aromatics with the concentration of 53.1–65.9 area%). Both SO2/H2O and CH3OH/H2O show high liquid-liquid extraction efficiency to concentrate the benzenoid aromatics for 3.4–11.0 times. This work shows the fast pyrolysis followed by liquid-liquid extraction for the valorization of paper sludge, of which the former has been recently demonstrated on a pilot-scale unit in industry. However, the latter still needs to be further developed by, e.g., focusing on the extraction solvent and continuous liquid-liquid extraction process integrated to fast pyrolysis.
摘要:造纸污泥是造纸业的固体废弃物,通常采用填埋、堆肥和焚烧等方式处理。造纸污泥含有造纸填料和木质纤维素生物质,二者均可通过热化学回收技术(如快速热解)实现资源化利用,以回收循环矿物质并生产生物基燃料和化学品,推动循环生物经济发展。本文通过热重分析、水分分析、灰分分析、CHNS元素分析、粉末X射线衍射和X射线荧光光谱法,对采集自荷兰和西班牙的三种不同造纸污泥样品进行了表征。在实验室规模的连续搅拌釜式反应器中,于500±10°C、进料速率1kg h⁻¹条件下对造纸污泥进行快速热解。循环矿物质(主要为碳酸钙)的回收率达到87.1±2.2%(以矿物质为基础)。快速热解生物液体和生物炭的产率分别为49.2±6.7wt%(以生物质为基础,相当于污泥干基的23.7±2.2wt%)和23.8±8.3wt%(以生物质为基础)。快速热解生物液体为稀释的水相混合物,含有多种含氧化合物(主要包含醇类、酸类、苯环类芳香族化合物、醛类、酮类、醚类和酯类)及烃类。进一步采用CH₃OH/H₂O和SO₂/H₂O对热解生物液体进行液-液萃取,获得了目标生物基化学品(即苯环类芳香族化合物,浓度达53.1–65.9area%)浓度显著提升的改良生物油。两种萃取剂均表现出高效的富集能力,使苯环类芳香族化合物的浓度提升至原有的3.4–11.0倍。本研究展示了通过快速热解结合液-液萃取实现造纸污泥价值提升的路径,其中快速热解已在工业中试装置得到验证,而液-液萃取技术仍需进一步发展,例如优化萃取溶剂、开发与热解集成的连续萃取工艺。


