Vikla, A. K.K., Simakova, I., Demidova, Y., Keim, E. G., Calvo, L., Gilarranz, M. A., Songbo He*, Seshan, K
Applied Catalysis A, General, 2021, 610:117963
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2020.117963
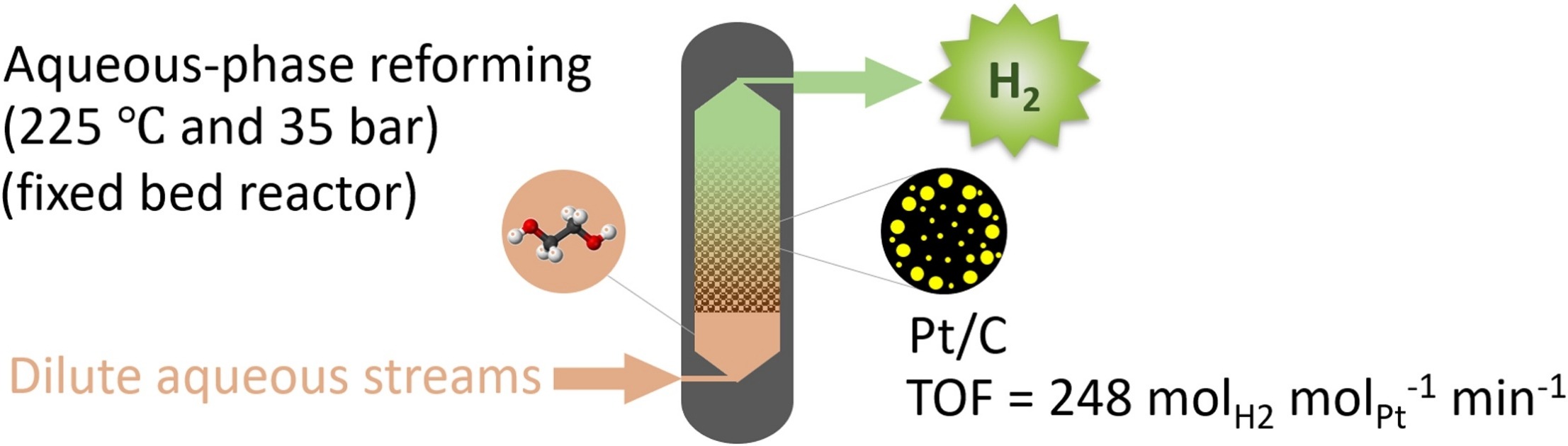
ABSTRACT: Pt/C catalysts with varied Pt sizes and distributions were investigated for aqueous-phase reforming (APR) of ethylene glycol (EG) to H2. APR experiments were performed on a continuous-flow fixed bed reactor with a catalyst loading of 1 g and EG feeding of 120 mL h−1 at 225 °C and 35 bar for 7 h. The fresh and used Pt/C catalysts were characterized by XRF, BET, CO chemisorption, TEM, XTEM, and XPS. Catalyst preparation protocols changed Pt characteristics on Pt/C catalysts, leading to a distinguishable H2 production. The rates for EG conversion and H2 production increased linearly with mean Pt size (3–11 nm), while having a volcano relationship with the mean size of agglomerated Pt particles (17–30 nm). Pt with concentrated Pt particles on surface of Pt/C catalysts was more preferable for APR of EG than the homogeneously distributed in catalysts. Optimal performance was obtained over a Pt/C-PR catalyst, which was prepared by precipitation method, showing a superb turnover frequency of 248 molH2 molPt−1 min−1 for H2 production from EG in APR. Besides, Pt/C catalysts also showed excellent stability. These results have shown the promise of Pt/C catalyst for APR of EG, which can be extended for bio-H2 production via APR of biomass-derived oxygenates in waste streams.
摘要:本研究通过调控Pt/C催化剂中铂的尺寸与分布,考察其对乙二醇水相重整制氢性能的影响。在连续流动固定床反应器中,于225°C、35 bar条件下,以1 g催化剂负载量和120 mL/h乙二醇进料速率进行7小时水相重整实验。利用XRF、BET、CO化学吸附、TEM、XTEM和XPS等技术对新鲜及使用后的Pt/C催化剂进行表征。结果表明,制备方法可通过改变铂的尺寸与聚集状态显著影响制氢性能:乙二醇转化率和氢气产率随铂平均粒径(3–11 nm)增大呈线性上升趋势,而与铂聚集体平均尺寸(17–30 nm)呈现火山型关系。表面铂颗粒集中分布的催化剂优于均匀分布体系,其中沉淀法制备的Pt/C-PR催化剂性能最优,其产氢转换频率高达248 molH₂/molPt/min,且所有催化剂均表现出良好稳定性。该研究证实Pt/C催化剂在乙二醇水相重整制生物氢能中的潜力,可进一步推广至生物质衍生含氧化合物废弃物转化体系。


