Khalid Khazzal Hummadi*, Sha Luo, Songbo He*
Chemosphere, 2022, 287: 131907
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131907
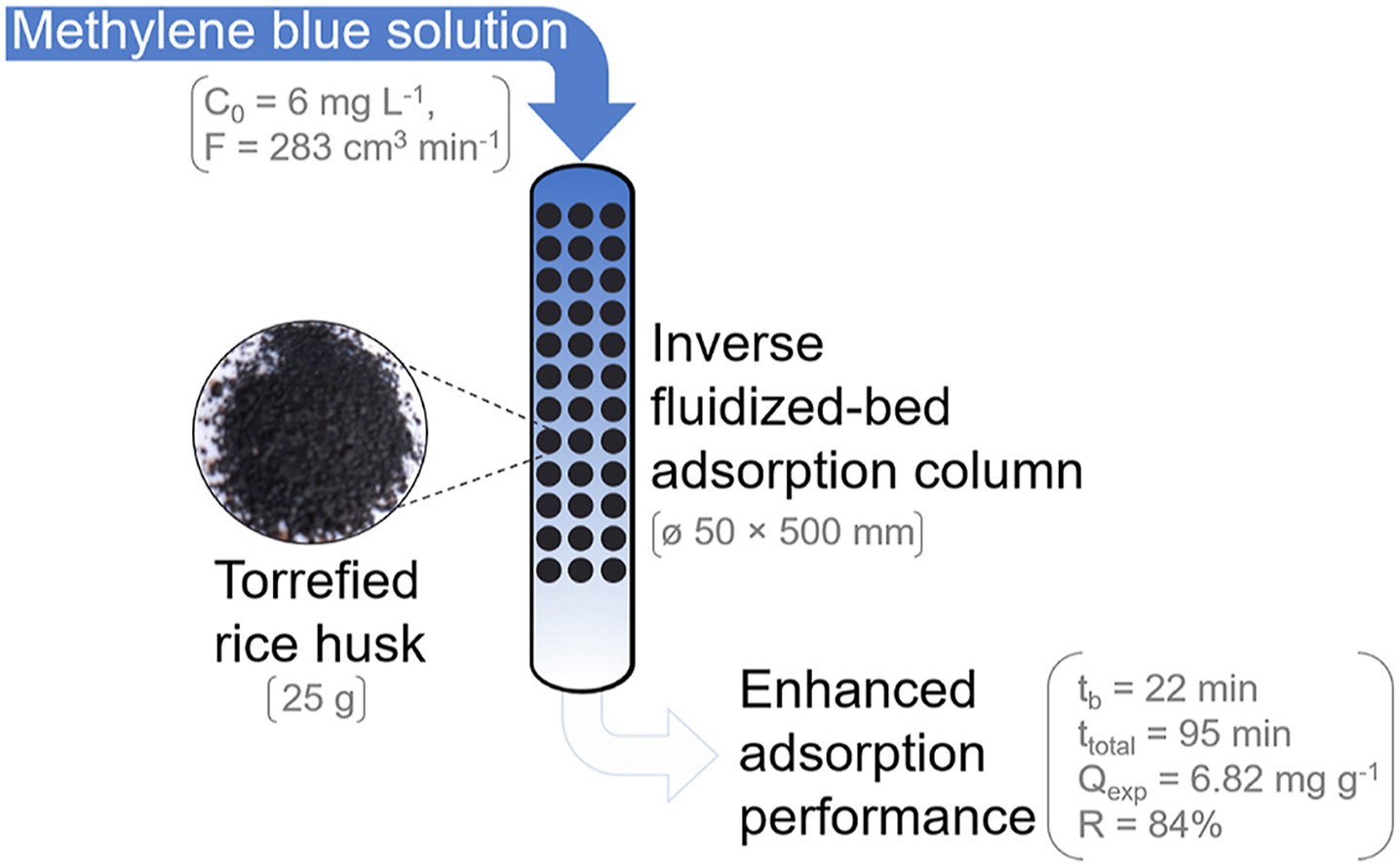
ABSTRACT: In this work, the inverse fluidized-bed bio-adsorption column is applied for the first time and is demonstrated using the torrefied rice husk (TRH) for the removal of methylene blue from the solution. The bio-adsorbents were characterized by BET, FI-IR, and SEM. The inverse fluidized-bed adsorption column using TRH becomes saturated in the 95-min continuous adsorption, during which the breakthrough time is 22 min, the overall MB removal (R) is 84%, and the adsorption capacity (Qexp) on the TRH is 6.82 mg g−1. These adsorption characteristics are superior to those in the fixed-bed adsorption column (R of 52% and Qexp of 2.76 mg g−1) at a lower flow rate (100 vs. 283 cm3 min−1). Torrefaction of RH significantly increases the surface area (28 vs. 9 m2 g−1) and enhances the surface functional groups, leading to an improved maximum equilibrium adsorption amount from 21.5 to 38.0 mg g−1 according to Langmuir model in the batch adsorption system. Besides, the increased Qexp on the TRH is also obtained in the inverse fluidized-bed (5.25 vs. 2.77 mg g−1, 89% higher) and the fixed-bed (2.76 vs. 1.53 mg g−1, 80% higher) adsorption columns compared to that on the RH.
摘要:本研究首次应用反向流化床生物吸附柱,以焙烧稻壳(TRH)为吸附剂去除溶液中的亚甲基蓝。通过BET、FI-IR和SEM对生物吸附剂进行了表征。在连续吸附95分钟内,使用TRH的反向流化床吸附柱达到饱和,其穿透时间为22分钟,总亚甲基蓝去除率(R)为84%,TRH的吸附容量(Qexp)为6.82 mg g⁻¹。这些吸附特性优于在较低流速下运行的固定床吸附柱(R为52%,Qexp为2.76 mg g⁻¹,流速分别为100 cm³ min⁻¹ 和283 cm³ min⁻¹)。稻壳的焙烧处理显著增加了其比表面积(从9 m² g⁻¹提高至28 m² g⁻¹)并增强了表面官能团,根据间歇吸附体系的Langmuir模型,最大平衡吸附量从21.5 mg g⁻¹提高至38.0 mg g⁻¹。此外,与原始稻壳相比,TRH在反向流化床(5.25 vs. 2.77 mg g⁻¹,提高89%)和固定床(2.76 vs. 1.53 mg g⁻¹,提高80%)吸附柱中也表现出更高的Qexp。


